Postmenopausal Bleeding
Going through menopause is a significant transition in a woman’s life. Your body is experiencing many changes at once as you move into the next phase of life.
However, one of the advantages that women experience during this time is the end of menstrual bleeding. Keep in mind: true menopause indicates that you have not had a period for a year. With that said, there are some instances in which women experience bleeding after menopause. Before we get into potential causes, according to a study by JAMA Internal Medicine, 90 percent of cases of postmenopausal bleeding are not due to a serious condition.
Common Reasons for Bleeding after Menopause
What causes bleeding after menopause? There are a number of conditions associated with postmenopausal bleeding. If you experience bleeding, it’s incredibly important to reach out to your doctor so you may identify the source of it.
Medications
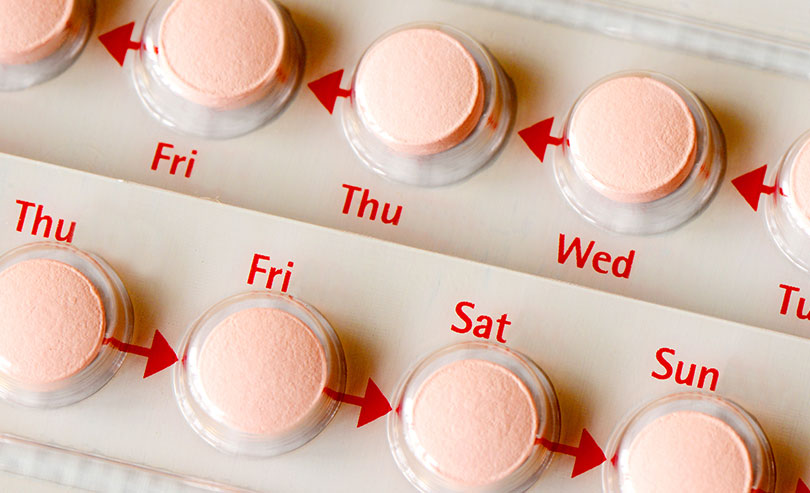
Sometimes bleeding after menopause is brought on simply by the medications you have been prescribed. A potential side effect of hormone replacement therapy is bleeding. Other medications that could cause postmenopausal bleeding are blood thinners and tamoxifen.
Vaginal Atrophy
Up to 40 percent of women experience menopause and vaginal atrophy. Vaginal atrophy involves the tissue surrounding the vagina becoming thin, dry and inflamed. This is often a result of lowered estrogen levels in the body which occurs because of menopause. Once the thinning occurs, it can lead to pain, swelling and bleeding especially after sexual intercourse.
Cancer
Bleeding is the number one sign of endometrial and uterine cancer following menopause. About 10 percent of postmenopausal women who experience bleeding do so because of endometrial cancer (uterine cancer).
Endometrial cancer most often affects postmenopausal women, according to the American Cancer Society. One of the first signs of this type of cancer is bleeding after menopause. This is why you should never ignore post-menopausal bleeding as it could be a sign of a serious condition.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Certain sexually transmitted such as chlamydia, gonorrhea and herpes can cause bleeding from the genitals. There are usually other physical signs as well (such as sores, foul odor, etc.). However, keep in mind, sometimes bleeding is the only symptom to occur.
Polyps
Polyps are a growth of tissue that can form in the uterus, cervix and cervical canal. While these growths are not typically cancer, they can cause spotting or heavy bleeding.
However there is an increased risk of the polyps being malignant or pre-malignant in postmenopausal women. This risk increases with age.
Endometrial Atrophy
The thinning of the endometrial tissue that lines the uterus may cause bleeding as the hormone levels in the body decrease.
Endometrial Hyperplasia
As the hormone levels in your body change, you may end up with too much estrogen and too little progesterone. This can cause endometrium thickening and result in bleeding. Cells may become abnormal which could indicate cancer. You should absolutely get this checked out to ensure that cancer is not the culprit.
Treatment Options
How is bleeding after menopause treated? Fortunately, there are many options available. Of course, the treatment will depend on the cause of the bleeding.
Estrogen Therapy
Vaginal and endometrial atrophy are often treated with estrogen therapy. Your doctor may prescribe this treatment in the following forms:
- Pills: Ingested orally
- Vaginal cream: Applied using an applicator
- Vaginal ring: Put in place by doctor. This releases estrogen for about three months.
- Vaginal tablet: Inserted using an applicator, daily or a few times a week
Progestin Therapy
This treatment is used to remedy endometrial hyperplasia. The doctor may prescribe it as a pill, cream or shot.
Hysteroscopy
A hysteroscopy will be conducted in the event that the bleeding is a result of polyps. A device will be inserted in the vagina, and then small surgical tools will be used to remove the thickened tissue.
Dilation and Curettage (D&C)
This surgery requires the doctor to open your cervix and remove polyps or other thickened areas. This may be done at a day clinic using a local anesthetic or at a hospital using general anesthetic depending on the location and size of the polyps.
Hysterectomy
This procedure is the total or partial removal of the uterus. This particular option is used in the event of cancer or as a cancer preventative.
Radiation or Chemotherapy
In the event that your bleeding stems from a form of cancer, then proper cancer treatments will be introduced. The most common forms of cancer treatments include radiation and chemotherapy.
Surgical menopause is triggered by an oophorectomy, which is the removal of the ovaries. This article goes over what to expect and treatment options.
Medications
Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to treat sexually transmitted diseases or other infections of the vagina. Such medications are used to remedy the disease source and will relieve pain, swelling and inflammation associated with those diseases as well.
How Is Bleeding Diagnosed?
There are several ways that your doctor may be able to identify the source of vaginal bleeding. Some of these ways include:
- Physical exam
- Biopsy
- Transvaginal ultrasound
Your doctor will have a better understanding of which tests are most appropriate based on your concerns and other symptoms.
When to Talk to a Doctor
Vaginal bleeding may not seem critical, but it is a symptom that you should never ignore. Remember, many of these conditions are painless, and the only sign is irregular bleeding.
During the premenopausal stage, irregular bleeding is normal. Your body is going through a lot of changes, and you may experience spotting, irregular periods or other symptoms.
Is it normal to bleed after menopause? Once you’ve gone through menopause, you should not experience bleeding for no reason. If you notice bleeding after menopause or premenopausal bleeding that lasts longer than three weeks, then you should discuss your options with your doctor.
Overview
Postmenopausal bleeding may be a sign of a significant health concern. If you notice any bleeding, then you should not ignore it. Reach out to your medical provider and allow them to conduct proper tests to identify the source.
A faster diagnosis means you will have the treatment you need. If you have more questions, reach out to your doctor right away for more information.